Flat Earth Map With Ice Wall
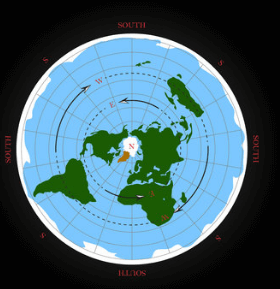
The concept of a Flat Earth Map With Ice Wall as a boundary, presents a fascinating divergence from traditional geographical models. This representation not only sparks debate regarding the validity of scientific evidence but also raises questions about the origins and evolution of such beliefs. As proponents articulate their rationale, the implications extend beyond mere cartography, challenging our understanding of physical reality itself. What motivates individuals to embrace this perspective, and how does it reflect broader societal trends? Exploring these questions reveals deeper layers of complexity in the ongoing discourse surrounding this contentious topic.
Read also: Elite Blood and Water
History of Flat Earth Map With Ice Wall Theory
The concept of a flat Earth has a long and complex history, deeply intertwined with the evolution of human thought and scientific understanding.
Ancient beliefs often depicted the Earth as a flat disc, reflecting the limited observational capabilities of the time.
However, modern misconceptions persist, fueled by misinformation and a rejection of established scientific principles, complicating the discourse surrounding Earth’s shape and our understanding of the universe.
The Flat Earth Map Explained
Flat Earth maps present a unique interpretation of global geography, reflecting the beliefs and assertions of those who subscribe to flat Earth theory.
These maps utilize various map projections to depict a flat, disc-like Earth, often placing the North Pole at the center and surrounding continents extended outward.
This representation challenges conventional geographic norms, appealing to those seeking alternative perspectives on global spatial understanding.
The Role of the Ice Wall
Central to the flat Earth model is the concept of an ice wall, which serves as a critical boundary that purportedly encircles the Earth’s disc.
Ice wall theories propose that this barrier prevents water from cascading off the edges, reinforcing boundary myths that challenge conventional scientific understanding.
Advocates argue that these walls symbolize both physical and ideological limits, inviting exploration of personal beliefs regarding Earth’s shape.
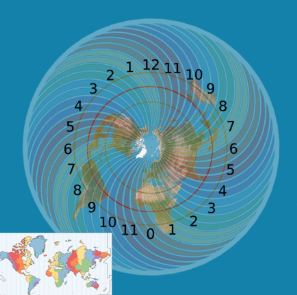
Implications for Geography and Science
Exploring the implications of a flat Earth model extends beyond theoretical boundaries, influencing geographical understanding and scientific principles.
This perspective fosters geographical misconceptions, challenging established cartographic conventions and navigation techniques.
Additionally, it stimulates scientific skepticism, prompting critical examination of empirical evidence.
Ultimately, engaging with such ideas invites discourse on the nature of knowledge, urging a reassessment of accepted norms within both geography and science.
Read also: Elon Musk Electricity Saving Invention
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Flat Earth Map With Ice Wall, serves as a profound symbol of the tension between belief and scientific understanding. This unconventional representation of Earth invites scrutiny and reflection on the nature of geographic knowledge. As discussions surrounding the validity of such theories persist, the ice wall stands as both a literal and metaphorical boundary, challenging the very foundations of accepted scientific paradigms and prompting a reevaluation of perspectives on the world’s structure.






